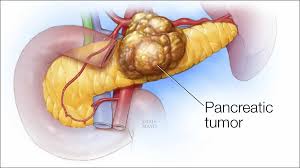
Pancreas is located in upper abdomen and is an essential organ of our body. Pancreas has two main functions:
Exocrine Functions: Secretion of enzymes – Helping in digestion
Endocrine Functions: Secretion of Hormones - Regulation of Blood Sugar
Types of Pancreatic Tumors
Exocrine tumors –
- Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
- Cystic neoplasms of pancreas – Mucinous and Serous Cystadenocarcinomas, IPMN
- Solid Pseudopapillary Neoplasms
- Acinar cell carcinoma
- Pancreatoblastoma
Endocrine tumors –
- Insulinoma
- Gastrinoma
- Glucagonoma
- VIPoma
- Somatostatinoma
Lymphoma
Carcinoma Pancreas –
- Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma(PDAC) is often referred to as carcinoma pancreas
- Most common type of pancreatic cancer (85%)
- Most common location of tumor is in head, ampullary and neck region of pancreas
- It is more common in men
- It is a very aggressive tumor
- Tumors of Head of pancreas, distal bile ducts and duodenum adjacent to ampulla behave similar with similar treatment pattern are considered together as Periampullary Tumors
Risk Factors –
- Smoking
- High energy diet rich in fat
- Chronic pancreatitis
- Familial pancreatitis
- Diabetes mellitus
- Occupational exposure to carcinogens like DDT, benzidine
- Hemochromatosis with pancreatic calcification
- Cirrhosis, obesity
- Genetic Causes -Peutz-Jegher syndrome, HNPCC (Hereditary Non-polyposis Colonic Cancer—Lynch II type), ataxia telangiectasia, hereditary breast and ovarian cancers, hereditary atypical multiple mole melanoma syndrome, familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP)
Clinical Features and Presentation
-
Jaundice – jaundice is severe, progressive, associated with itching
- Weight loss
- Loss of appetite
- Pain in abdomen
- Palpable lump
- Vomiting (Gastric outlet obstruction)
- Passage of yellow coloured urine and white coloured stools
Diagnosis of Pancreatic Cancer
To confirm pancreatic cancer, certain blood tests and imaging investigations are done.
Liver function tests
Tumor Markers-
Carcinoma embryonic Antigen (CEA) and Carbohydrate Antigen (CA19-9) are the tumor markers which are elevated in patients with carcinoma pancreas
Ultrasonography of Abdomen-
Ultrasound of abdomen is a good non-invasive investigation which is usually done in patients with jaundice and pain abdomen. It gives an idea regarding level of block of bile duct, location and size of mass lesion and presence of any metastasis.
Contrast enhanced CT of abdomen(CECT) and MRI abdomen-
To confirm the diagnosis of Cancer pancreas, a contrast enhanced CT scan with a pancreatic protocol should be done. It gives information regarding size, location and resectability status of tumor. It also gives information regarding involvement of adjacent structures and blood vessels, distant metastasis and thus help in planning of the surgery
Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS) and ERCP (Side viewing endoscopy) –
For taking biopsy of the tumor for histopathological examination and for confirmation of the diagnosis.
Definitive Treatment (Operable Cases):
-
For patients with resectable disease, Surgery is the best treatment option available.
-
For tumors in head and neck of pancreas, Whipple's Pancreaticoduodenectomy surgery is done.
- It involves removal of head and neck of pancreas with distal bile duct, duodenum, gall bladder and adjacent lymph nodes.
- For tumors of body and tail of pancreas, Distal Pancreatectomy surgery is performed. It includes removal of body and tail portion of pancreas. Removal of spleen may be required in cases close to tail of pancreas based on CT and surgery findings.
- For tumors involving whole of the pancreas, Total pancreatectomy is performed.
- For patients with a high bilirubin levels, ERCP and Biliary stenting is required to lower dowm bilirubin levels before surgery.
Palliative Treatment (Inoperable or Metastatic disease):
For patients with inoperable or metastatic disease, palliation of the symptoms is required
For Jaundice-
-
ERCP and Biliary stenting (Metallic /Plastic stent)
- Surgery – Roux en y Choledochojejunostomy
- Ultrasound Guided PTBD drainage
For Vomiting(Gastric outlet obstruction)-
- Endoscopy guided duodenal stenting
- Gastrojejunostomy
For Pain abdomen –
- Celiac axis block – Ultrasound guided blockade of nerves supplying pancreas/tumor which causes pain in abdomen.
- Opioids
- Palliative Radiotherapy
For patients with vomiting and jaundice and endoscopic access is not available due to tumor mass, surgery (Triple bypass) is the best method of palliation.
Chemotherapy:
Chemotherapy is given to patients with large tumor or lymph node positive disease after surgery. Adjuvant therapy using gemcitabine , 5FU have shown good response in these patients.
Neoadjuvant chemotherapy:
For patients, who are borderline resectable with involvement of vascular structures, neoajuvant chemotherapy/ chemoradiotherapy can be given to downsize the tumor and for improving the resectability status of the tumor.
 Pancreas is located in upper abdomen and is an essential organ of our body. Pancreas has two main functions:
Pancreas is located in upper abdomen and is an essential organ of our body. Pancreas has two main functions: 
